“Diabetes shouldn't hold you back from doing anything else any other kid can do.”
What is type 1 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is a lifelong disease that affects the body’s ability to convert glucose from food into energy. Without daily injections of insulin, people living with type 1 diabetes would not be able to survive.

Diogo is living with type 1 diabetes
Portugal
What are the symptoms of type 1 diabetes?
In most cases, type 1 diabetes develops early in life and is often diagnosed during childhood.
Signs of type 1 diabetes include:
- Excessive urination as your body expels excess glucose
- Extreme thirst resulting from urination
- Muscle cramps as fluid loss creates an imbalance in electrolytes in your blood
- Rapid weight loss as your body uses fat for energy when cells cannot absorb glucose
- Tiredness and fatigue as energy from glucose cannot reach your body’s cells
- Thrush/genital itching, yeast infections as glucose in urine provides a breeding ground for fungus and bacteria
- Blurry vision caused by high glucose levels in the fluid of your eye
- Sweet or fruity-smelling breath as acids are released when your body uses non-glucose energy sources
If you or a loved one experience any of these symptoms, please seek medical support immediately.
What causes type 1 diabetes?
The disease starts when the immune system attacks cells in the pancreas that produce insulin, the hormone that helps convert glucose into energy for the body’s cells. As more insulin-producing cells in the pancreas are destroyed, the body can no longer control its blood sugar levels and the symptoms of type 1 diabetes begin to appear.
Genetic and environmental factors are suspected to play a role in why a person develops type 1 diabetes.
Diagnosing type 1 diabetes
If you show signs of having type 1 diabetes, your doctor may use blood or urine tests to diagnose it. There are several ways this can be done. An initial test can be a simple blood sugar test. If your test results are above normal and you have the common symptoms, you may be diagnosed with type 1 diabetes.
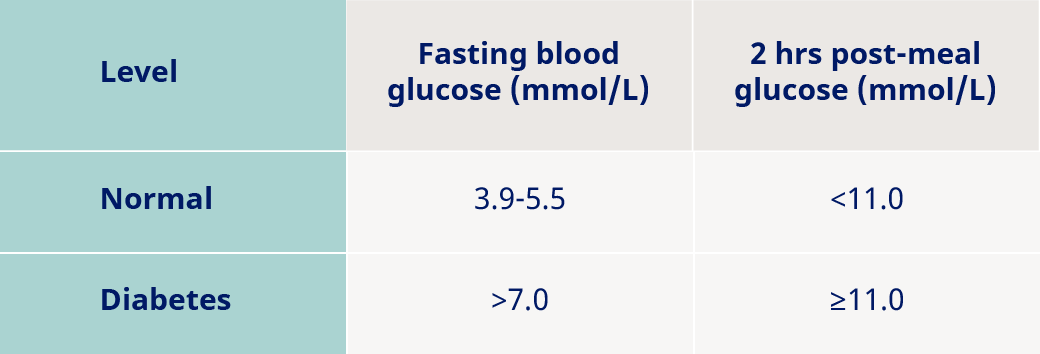
If you do not have the common symptoms but your blood sugar or urine blood sugar level is high, additional blood tests can be taken to measure HbA1C levels. HbA1C is a measure of how well controlled your blood sugar has been over a period of 3 months. It gives a good idea of how high or low, on average, your blood sugar levels have been. This chart compares normal levels with those indicating type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
Learn more about insulin, blood sugar and their effects on your body.
Living with type 1 diabetes
Since type 1 diabetes can develop quickly and without any clear warning signs, getting a diagnosis may come as quite a shock.
The best thing that you can do is take control of the situation and to learn as much as possible about type 1 diabetes, the treatment options and how it can affect daily life. Talk to your doctor for more information and advice. There are also many resources available for and by diabetes communities around the world. The more you know, the more prepared you will be to deal with the challenges ahead.
With good management of blood sugar levels and an overall healthy lifestyle, most people with type 1 diabetes can live a long and active life. Hear more about the experiences of someone with type 1 diabetes by clicking on the video below.



