Living with diabetes
How do you manage your lifestyle when it comes to diabetes? Whether it be nutrition or exercise, we have gathered tips and articles to help you manage your diabetes.
Your healthcare professional may recommend that you monitor when you start treatments that may cause you to have low blood sugar.
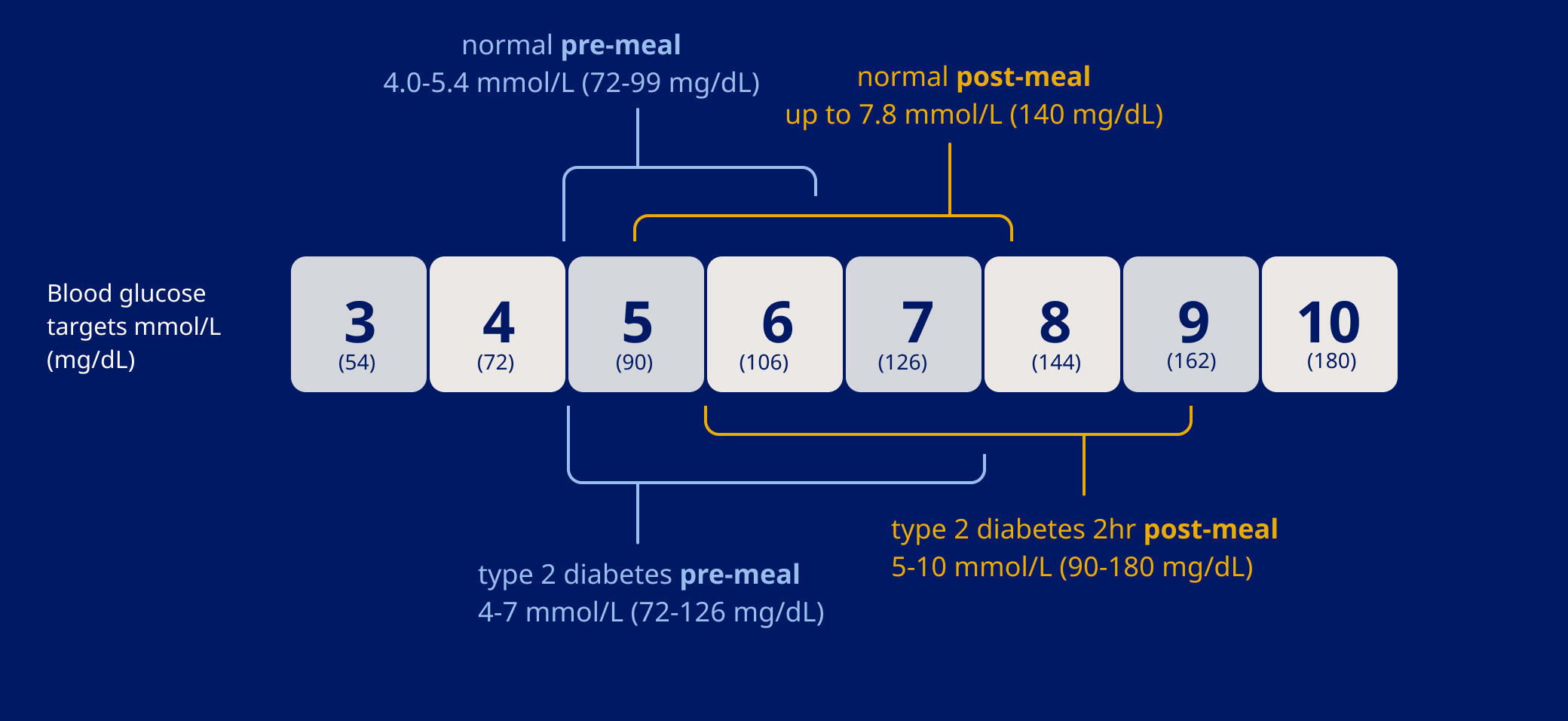
The following terms are used to describe glucose measurements taken at different times of day:
Checking in the morning before breakfast when your blood sugar is lowest
Checking right before a meal to see how much your levels change when you eat
Checking two hours after a meal when your blood sugar peaks
Keep in mind that a blood sugar check you perform yourself is not the same as the HbA1c test performed by your healthcare professional and the results cannot be compared.
Checking your blood sugar gives you a snapshot of your levels at a particular moment. Recording these measurements will help to show you your progress over time.
Accurately recording your blood sugar and what you eat, when you exercise, and emotional factors like stress, will help identify the causes of unusual peaks and dips. This may help you to improve your diabetes management.
There are many tools available to help you record your measurements, including diaries and smartphone apps. Read this article to learn how technology and digital health can improve diabetes management. And talk to your healthcare professional about the right option for you.
The average blood sugar ranges for people with and without type 2 diabetes can be seen below.11